
The Rogers Commission offered NASA nine recommendations that were to be implemented before shuttle flights resumed. They also disregarded warnings from engineers about the dangers of launching posed by the low temperatures of that morning and had failed to adequately report these technical concerns to their superiors.

NASA managers had known that contractor Morton Thiokol’s design of the SRBs contained a potentially catastrophic flaw in the O-rings since 1977, but they failed to address it properly. The Rogers Commission found that NASA’s organizational culture and decision-making processes had been a key contributing factor to the accident. The disaster resulted in a 32-month hiatus in the shuttle program and the formation of the Rogers Commission, a special commission appointed by United States President Ronald Reagan to investigate the accident.
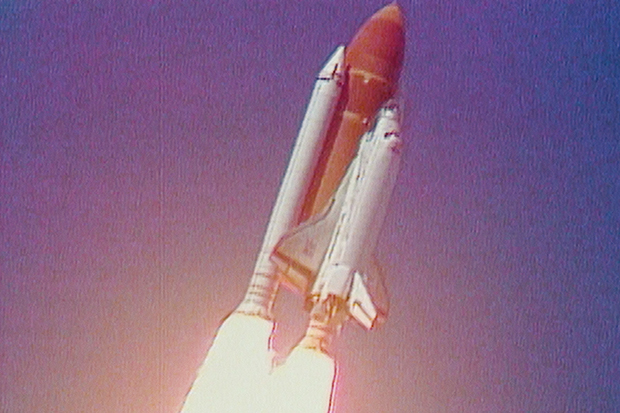
Aerodynamic forces promptly broke up the orbiter. This led to the separation of the right-hand SRB’s aft attachment and the structural failure of the external tank. The O-ring failure caused a breach in the SRB joint it sealed, allowing pressurized hot gas from within the solid rocket motor to reach the outside and impinge upon the adjacent SRB attachment hardware and external fuel tank.

The spacecraft disintegrated over the Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of central Florida, United States, at 11:39 a.m.ĭisintegration of the entire vehicle began after an O-ring seal in its right solid rocket booster (SRB) failed at liftoff. The Space Shuttle Challenger disaster occurred on January 28, 1986, when Space Shuttle Challenger broke apart 73 seconds into its flight, leading to the deaths of its seven crew members.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
